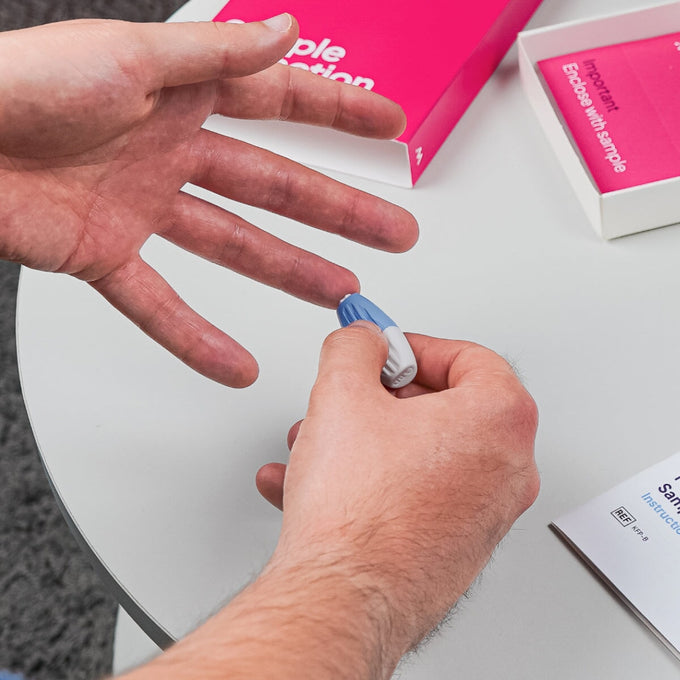
Advanced Thyroid Function Blood Test, from our experts to you.
Dr Sam Rodgers MBBS, MRCGPChief Medical Officer

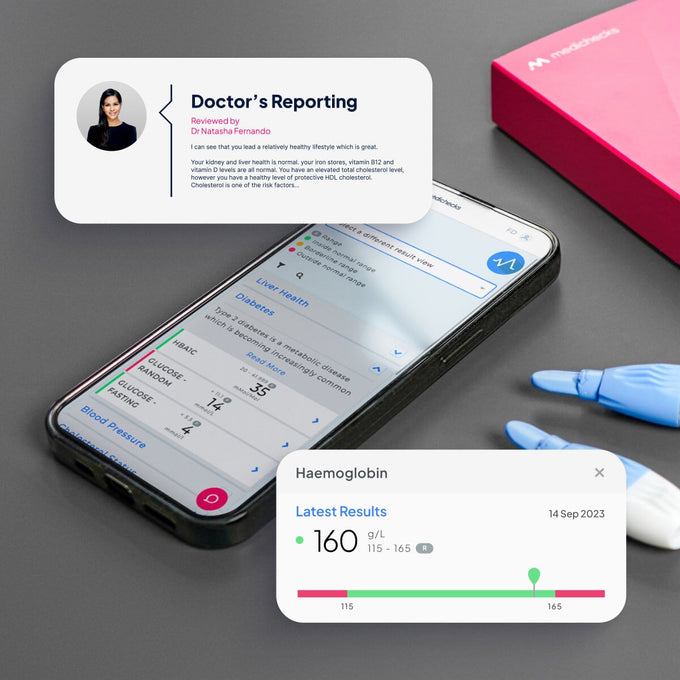
What is the Advanced Thyroid Function Blood Test?
Our Advanced Thyroid Function Blood Test is our most comprehensive thyroid test and contains everything you need to give you a clear picture of your thyroid health. It tests how well your thyroid is functioning and whether an autoimmune disorder could be causing your symptoms.
What can I learn from this test?
Why check for vitamins and minerals?
Our advanced profile includes relevant vitamins and minerals which support your thyroid function and can mimic the symptoms of an underactive thyroid if they are low. We have included tests for vitamin D, vitamin B12, folate (vitamin B9), and ferritin (a marker for iron storage). We also test an inflammation marker to help interpret your iron (ferritin) result and to give a picture of whether an autoimmune condition is causing inflammation in your body.
What's Included?
How to prepare for your test
Special Instructions
Prepare for your Advanced Thyroid Function Blood Test by following these instructions. Please take your sample before 10am. Take this test when any symptoms of short-term illness have settled. You should take this test before you take any medication or vitamin/mineral supplements. Do not take biotin supplements for two days before this test, discuss this with your doctor if it is prescribed. Do not take vitamin B12 for two weeks prior to this test. If your B12 is prescribed ask your doctor whether to stop.
Frequently asked questions
How do you test your thyroid?
If you are experiencing thyroid-related symptoms, such as changes with your weight, energy, mood, skin or hair, then a thyroid blood test will help you to test your thyroid function. We have three popular thyroid tests to help you understand whether you have the right level of thyroid hormones for a healthy metabolism.
What is the best blood test for thyroid?
Private thyroid tests can give you access to the full range of thyroid hormones, thyroid antibodies and nutrients that can affect your thyroid health, together with the added advantage of a convenient and speedy service. The blood tests available from your GP often only routinely test your thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (FT4).
Look at the different types of thyroid blood tests with our Thyroid Buying Guide.
Does fasting affect thyroid blood test?
In general, you do not need to fast before a thyroid blood test. If you are required to fast, you will be told in advance. It is best to fast overnight and take your test in the morning so that you don’t have to go too long without eating.
It is, however, very important to make sure that you are well-hydrated before taking a blood test. Read our top tips for taking a finger-prick blood test or look at our Frequently Asked Questions for more information.
How do you test for underactive thyroid?
The best way to test for an underactive thyroid is through a thyroid blood test. However, it isn’t always enough to just focus on thyroid function. Symptoms which may be associated with an underactive thyroid could also be caused by other conditions such as iron deficiency anaemia, a nutritional deficiency or a hormone imbalance.
To diagnose an underactive thyroid, your doctor will look at your symptoms together with the results of blood tests that measure the level of your thyroid hormones.