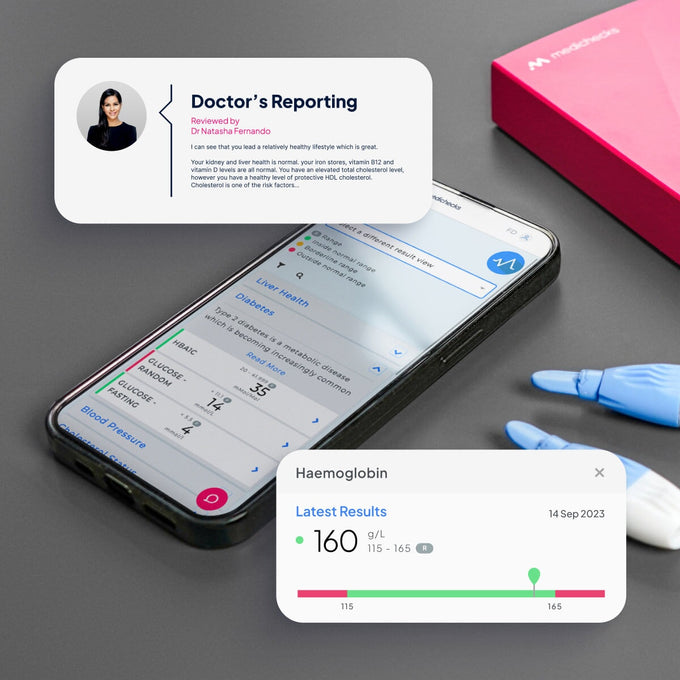
Full Blood Count (FBC) Blood Test, from our experts to you.
Dr Sam Rodgers MBBS, MRCGPChief Medical Officer

What is an FBC?
Our Full Blood Count (FBC) blood test, also known as a Complete Blood Count (CBC) or Haematology profile, is routinely used by doctors to examine the health of your red, white, and clotting blood cells.
Why check my red blood cells?
Red cells are vital for transporting oxygen around the body, and anything that affects their ability to do so can lead to symptoms, including fatigue. An FBC looks at the size, shape, and volume of your red blood cells and will help assess whether you are suffering from anaemia, either caused by a deficiency in iron or vitamin B12.
What can I learn from my white blood cells?
White blood cells are key to supporting your body's immune system and can indicate whether you are suffering from or have recently suffered from an injury or infection.
What's Included?
Frequently asked questions
What is a Full Blood Count Blood Test?
A Full Blood Count Blood Test, or a haematology profile, is a routine test to check your general health and immune function. Generally, it is for people who have a history of blood disorders, are experiencing symptoms of low iron or would like to check their white blood cell count for, or after, an infection or inflammation.
What does a Full Blood Count Blood Test look for?
By examining the components of blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets, a FBC tests for abnormalities in your blood. This can indicate infection or inflammation in the body and check for anaemia, which can either be caused by iron or vitamin B12 deficiency.
Can a Full Blood Count Blood Test detect diabetes?
A full blood count test is not used to detect diabetes. The two types of blood tests used to detect diabetes are the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, which measures blood sugar after you’ve fasted for 8 hours, and the HbA1C blood test, which identifies blood sugar levels over the previous 8-10 weeks.
If you believe you are at risk of developing diabetes, you can test your blood sugar levels with our simple finger-prick, Diabetes (HbA1C) Blood Test.
How long does a Full Blood Count Blood Test take?
Blood test results can take anything from a few hours to a few weeks to be processed, depending on whether you go through the NHS, a private specialist or a digital consumer health company. Our full guide to blood testing explains exactly how blood testing works.