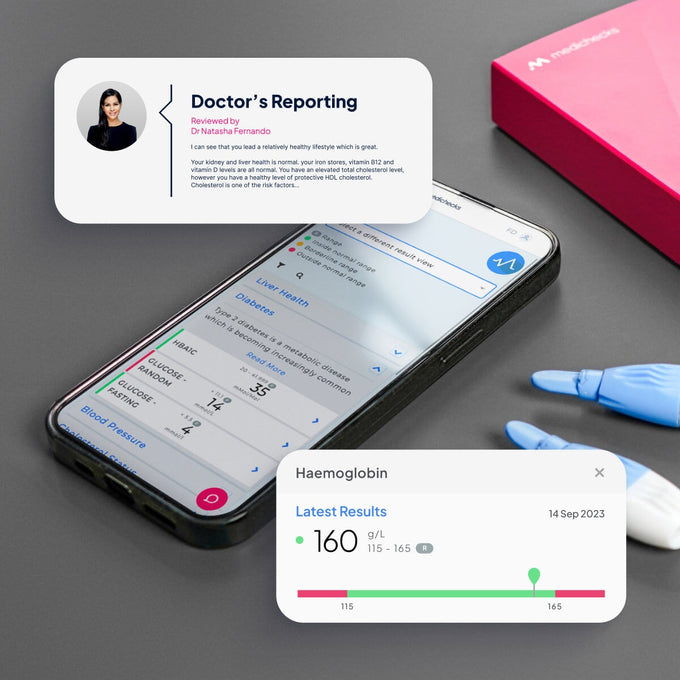
Immunoglobulins IgG IgM IgA Blood Test, from our experts to you.
Dr Sam Rodgers MBBS, MRCGPChief Medical Officer

What are antibodies?
Antibodies (also known as immunoglobulins) support the immune system, helping protect the body against non-self and harmful bacteria, viruses, and substances. There are five different classes of immunoglobulins and several subclasses. Each class represents a group of antibodies that has a slightly different role.
What can I learn from this test?
Our test measures the amount of immunoglobulins A, G, and M (IgA, IgG, IgM) in your blood. This allows you to detect or monitor an excess or deficiency in one or more immunoglobulin classes.
What are immunoglobulins A, G, and M?
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies are produced as a first response to a new non-self antigen, providing short-term protection. Then, immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are produced during the initial infection. Around 70-80% of the immunoglobulins in the blood are IgG, and your body retains a catalogue of these antibodies to rapidly reproduce them whenever exposed to the same antigen. IgG antibodies form the basis of long-term protection against microorganisms. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies comprise about 15% of the total lung and stomach secretions and breast milk. IgA protects against infection in mucosal areas of the body, which are the soft tissue that lines your body's canals and organs in the digestive, respiratory, and reproductive systems.